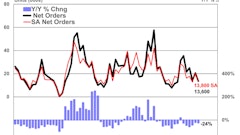
The unemployment rate in construction dropped to the lowest April level in seven years as contractors added 32,000 workers to payrolls, bringing industry employment to 6.0 million. It’s the highest level of construction employment since June 2009, according to an analysis of new government data by the Associated General Contractors of America.
“It is heartening that all categories of construction employers added workers, not only in April but over the past 12 months,” said Ken Simonson, the association's chief economist. “Moreover, contractors have been adding to workers’ hours as well as hiring more employees,”
Construction employment totaled 6,000,000 in April, a gain of 189,000 or 3.3 percent from a year earlier, while aggregate hours worked rose even more—3.8 percent, Simonson noted. Residential building and specialty trade contractors added a combined total of 13,100 workers in April and 107,900 (5.0 percent) over 12 months.
Nonresidential construction—building, specialty trades and heavy and civil engineering contractors—grew by 18,600 employees last month and 81,300 (2.2 percent) since April 2013.
“There is a limit to how much overtime workers can put in, and companies will be seeking to expand employment even faster if the volume of projects continues to grow,” Simonson added. “But the huge drop in the number of unemployed former construction workers may make it harder to keep adding employees.”
The unemployment rate for workers actively looking for jobs and last employed in construction declined from 13.2 percent a year earlier to 9.4 percent last month. Simonson noted that the unemployment rate for construction workers had fallen by more than half since April 2010, when it reached 21.8 percent. During that time, the number of unemployed workers who last worked in construction declined by 1.1 million, but industry employment increased by less than 450,000.
Association officials said that a sharp drop in the number of secondary-level construction training programs over the past several years has contributed to a decline in new entrants to the industry to replace retiring workers. They urged federal, state and local officials to adopt measures to help schools, construction firms and local trade associations to start and expand training programs for future construction workers.
“If elected and appointed officials don’t act soon to improve the quantity and quality of training opportunities for future workers, many construction employers will struggle to find the workers they need,” said Stephen E. Sandherr, the association’s chief executive officer. “It would be tragic if the construction industry can’t fill good-paying jobs because of a lack of trained recruits.”